The HATS Stage 2A project expands Drainage Services Department’s facilities for treatment of 70% of the HKSAR’s sewage. The works include upgrading of Stonecutters Island Sewage Treatment Works (SCISTW) and Preliminary Treatment Works (PTWs) in the northern and southwestern parts of Hong Kong Island, and construction of the related Sewage Conveyance System. SCISTW is one of the world’s largest chemically enhanced primary treatment facilities. Its treatment capacity is 2.45 million cubic metres per day, and serves up to 5.7million people. The full commissioning of the HATS project greatly improves water quality in Victoria Harbour and surrounding near-shore areas, and enables the sustainable development of the harbour area.
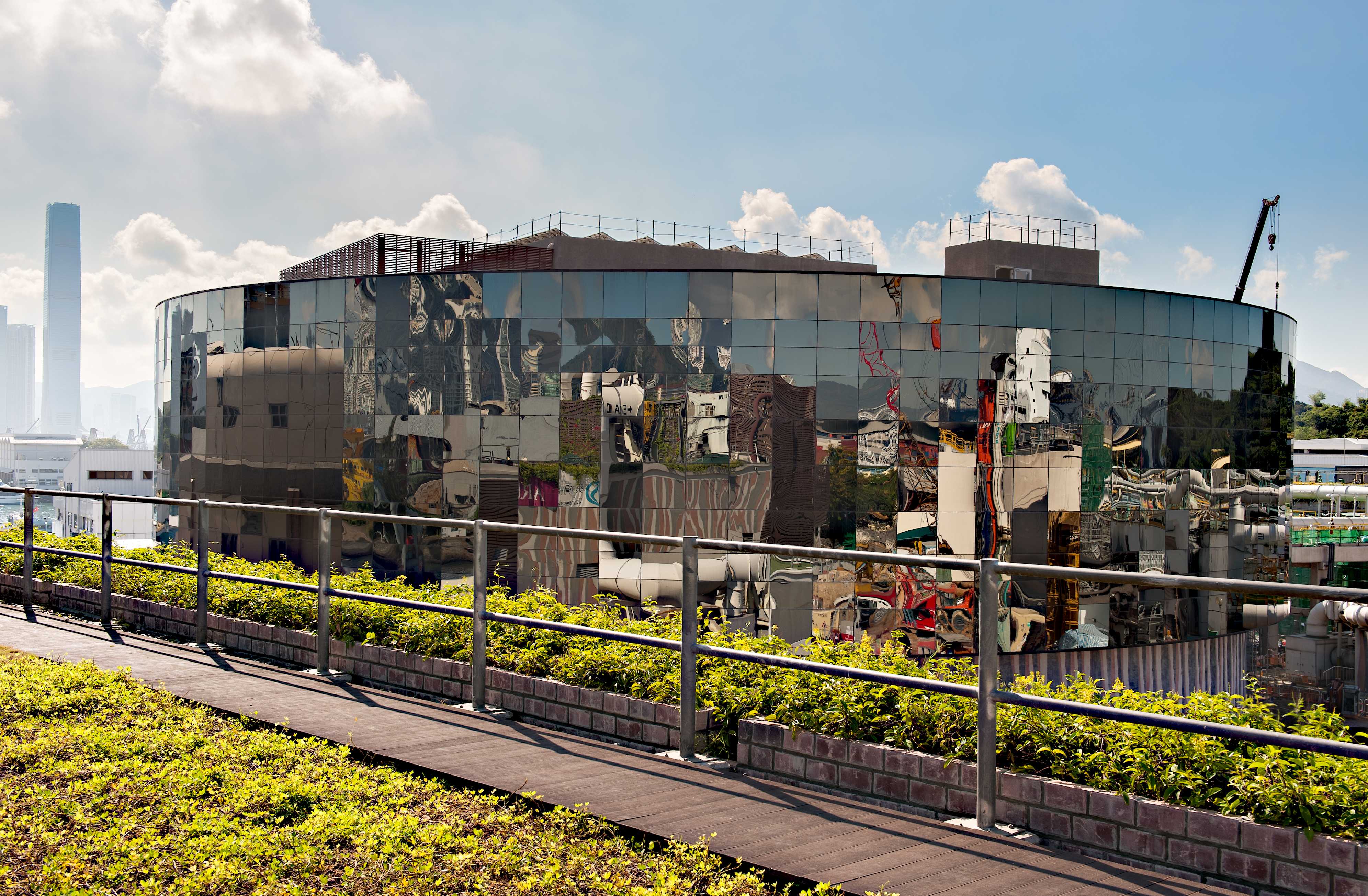

Main Pumping Station No. 2 (MPS2) at SCISTW is one of the World’s largest underground sewage pumping stations. MPS2 is circular on plan, with an internal diameter of 55m and depth of 40m.
8 sets of sewage pumps have been installed inside MPS2, each with a capacity of 4m³/s. The combined capacity can fill up a standard swimming pool less than 1 minute.

An interconnection tunnel links the two main pumping stations. This enhances operational flexibility and system robustness.
The interconnection tunnel was constructed using a tunnel boring machine. Artificial ground freezing techniques with brine were adopted to stabilize the surrounding soil mass for key interface areas. This is the first time that such methods have been adopted in Hong Kong.

Marine Vessels (Clean Harbour 1&2) deliver all sludge from SCISTW to the Sludge Treatment Facility to minimize the traffic and environmental impacts compared with land transportation.
The vessels adopt “Diesel-electric propulsion”, with onshore power supply when berthed. No combustion of fuel is required during berthing, and therefore zero emissions can be achieved.